What is Kanban?
Kanban is a new method for managing knowledge work with an emphasis on just-in-time delivery while not overloading the team members. According to David J. Anderson, it is an approach to incremental, evolutionary process and systems change for organizations. It is a way to organize the chaos that surrounds so many delivery teams by making the need for prioritization and focus clear. It is a way to uncover workflow and process problems so you may solve them in order to deliver more consistently to your client or customer. In this approach, participants have the possibility to see the process from definition of a task to its delivery to the customer.
In the case of software development, Kanban can mean a visual process-management system that tells what to produce, when to produce it and how much to produce. It is inspired by the Toyota Production System and by Lean manufacturing. Software development is a creative activity and different to mass-producing cars but the underlying mechanism for managing the production line can still be applied.
Kanban has 9 things you must know. They are rooted in four basic principles and five properties.

The basic principles of Kanban
- Start with what you do now
The Kanban method does not prescribe a certain setup or procedure. The Kanban method starts with existing roles and processes and stimulates continuous, incremental and evolutionary changes to the system.
You can overlay Kanban properties on top of your existing workflow or process to bring your issues to light so that you can introduce positive change over time. This makes it very easy to begin a Kanban implementation as you do not have to make sweeping changes.
- Agree to pursue incremental, evolutionary change
The Kanban method is an approach to change management that is designed to meet minimal resistance. Therefore it encourages continuous small incremental and evolutionary changes to your current system. Sweeping changes are discouraged because they generally encounter increased resistance due to fear or uncertainty.
- Respect the current process, roles, responsibilities and titles
The Kanban method seeks to drive out fear in order to facilitate future change. It attempts to eliminate initial fears by agreeing to respect current roles, responsibilities and job titles with the goal of gaining broader support.
- Encourage acts of leadership at all levels
This principle is something that is espoused in many methodologies and the Kanban method is no exception. You don’t need to be a team lead or an executive to be a leader. Some of the best leadership comes from everyday acts from people on the front line of their respective teams. Everyone needs to be fostering a mindset of continual improvement to reach your optimal performance as a team. This can’t be a management level activity.
Core properties
David Anderson identified five core properties that he consistently observed in successful implementations of the Kanban method.
- Visualize the workflow
You can’t improve what you can’t see. Knowledge work needs a way to show progress. Kanban boards are one of the ways to display progress. The most common way to visualize your workflow is to use card walls with cards and columns. Each column on the wall represents steps in your workflow.
The most common way to visualize your workflow is to use card walls with cards and columns. Each column on the wall represents steps in your workflow.
- Lead using a team approach
Without a team and leadership, nothing of significant value can be created or improved.
- Reduce the Batch Size of your Efforts or Reduce BASE
Science and the work from Donald G. Reinertsen has shown that when the batch unit of work is decreased, more can be accomplished. This principle goes beyond simply Limiting Work in Progress.
- Lean and improve continuously
This practice implies reflecting so that one can learn from experience, and it aligns with performing retrospectives and embracing Kaizen. In addition Open Kanban itself is open source and it welcomes contributions or extensions to the method.
Worked Example
The board below shows a situation where the developers and analysts are being prevented from taking on any more work until the testers free up a slot and pull in the next work item. At this point the developers and analysts should be looking at ways they can help relieve the burden on the testers.
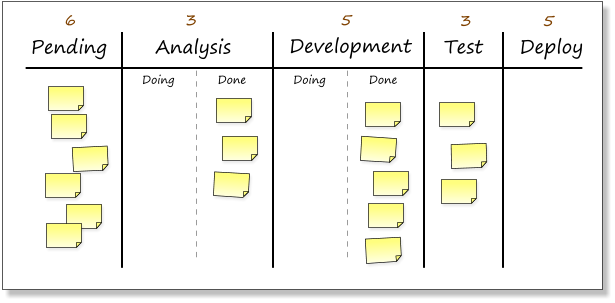
Some of the columns are split in two, to indicate items being worked on and those finished and ready to be pulled by the downsteam process. The limits at the top of the split columns cover both the “doing” and “done” columns.
Once the testers have finished testing a feature, they move the card and free up a slot in the “Test” column.
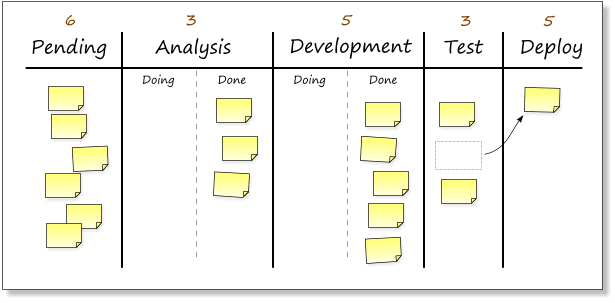
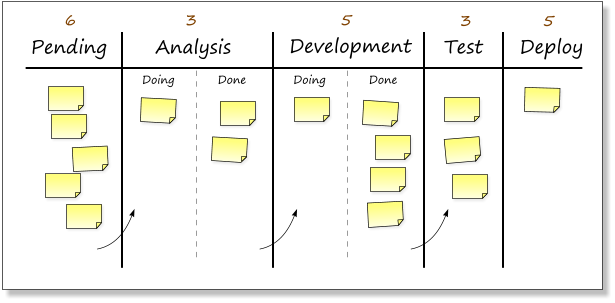
The empty slot in the “Test” column can then be filled by one of the cards in the development “done” column. That frees up a slot under “Development” and the next card can be pulled from the “Analysis” column and so on.
How to get started with Kanban
First of all you have to map your value stream. After that you define the start and end points for the Kanban system, agree, draw up a Kanban board and start using it.
To summarize, Kanban is a perfect method for managing software development process. A great tool that helps manage projects using Kanban boards is Trello.com, which we widely used by our team at Razor Theory.